IPv4
An IP address is a software address, not a hardware address consists
of 32 bits of information. These bits are divided into four sections,
referred to as octets or bytes, each containing 1 byte (8 bits). An IP
address is a numeric identifier assigned to each machine on an IP
network.
Octet: An octet, made up of 8 bits, is just an ordinary 8-bit binary
number.
Internet Protocol Architecture
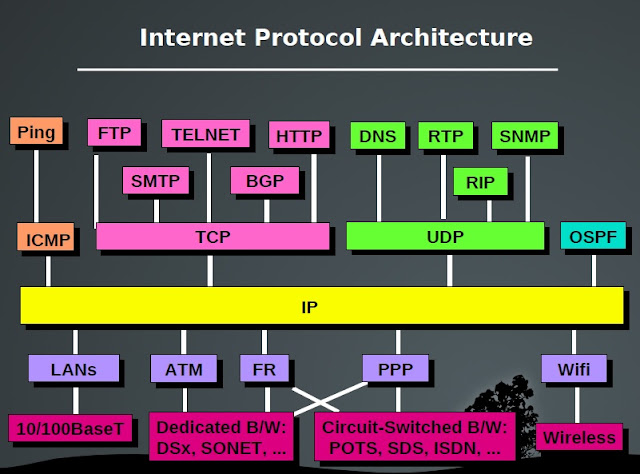 |
| Internet Protocol Architecture |
IPv4 Packet Structure
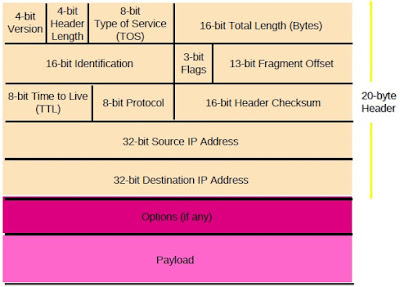 |
| IPv4 Packet Structure |
Dotted-decimal notation
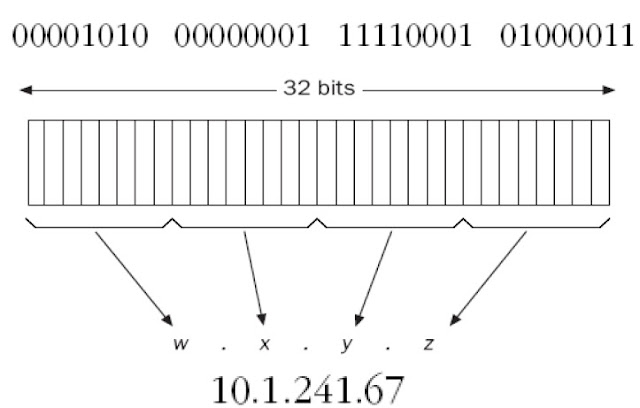 |
| Dotted-decimal notation |
Hexadecimal Notation
 |
| Hexadecimal Notation |
Converting from Binary to Decimal
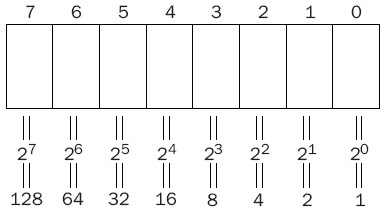 |
| Converting from Binary to Decimal |
For example, the 8-bit binary number 01000011 is 67 (64 + 2 + 1).
The maximum number that can be expressed with an 8-bit number (11111111) is 255
(128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1)
IP Classification
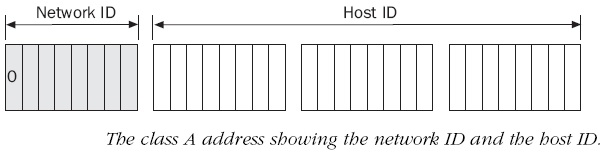
Class-A :
IP address scheme said that the first bit of the first byte in a Class A network address
must always be off, or 0. This means a Class A address must be between 0 and127 in
the first byte, inclusive.
0xxxxxxx
If we turn the other 7 bits all off and then turn them all on, we’ll find the Class A
range of network addresses:
00000000 = 0 to 01111111 = 127
0 and 127 are not valid in a Class A network.
0 is no fill in first octet and 127 is loop back ip
 |
| IP class A |
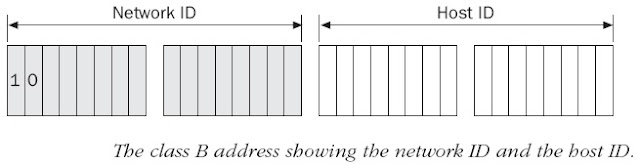
Class B
the first bit of the first byte must always be turned
on but the second bit must always be turned off. I you turn the other 6 bits all off
and then all on, you will find the range for a Class B network:
10000000 = 128 to 10111111 = 191
 |
| Class B IP Addresses |
This class is used for medium-sized networks.
A good example is a large college campus.
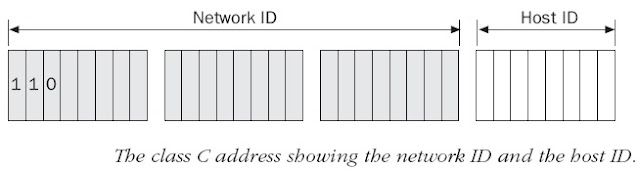
Class C
the first 2 bits of the first octet as always turned on,
but the third bit can never be on.
11000000 = 192 to 11011111 = 223
 |
| Class C IP Addresses |
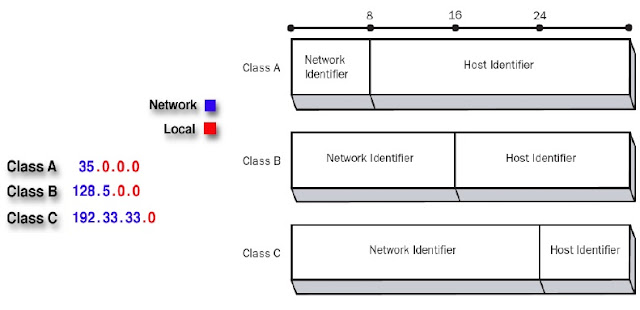
Examples of IP Class A, B and C
 |
| IP Class A,B and C |
Classes D and E
The addresses between 224 to 255 are reserved for Class D and E networks.
Class D (224–239) is used for multicast addresses
Class E (240–255) for scientific purposes .
Reserved IP Addresses
1. 127.0.0.1 Reserved for loopback tests. This means that it is used by the host
computer to send a message back to itself.
2.Network ID , when all host bits are zero(0) OFF
3.Broadcast ID , when all host bits are one (1) ON
IP Version 4 Properties
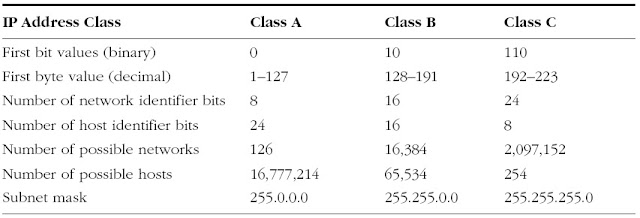 |
| IP Version 4 Properties |
Subnet Mask
A subnet mask is a 32-bit value that allows the recipient of
IP packets to distinguish the network ID portion of the IP
address from the host ID portion of the IP address.
A subnet mask separates the IP address into the network
and host addresses.
It is called a subnet mask because it is used to identify
network address of an IP address by performing bitwise
AND operation on the netmask.
 |
| Subnet Mask |
Properties of IP classes
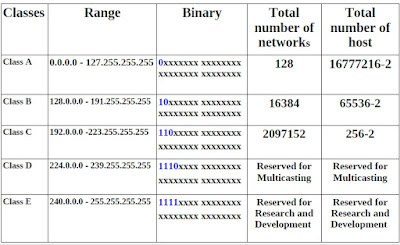 |
| Properties of IP classes |
public IP address
IP addresses that are visible to the public.
Public IP Addresses (also known as Static IP Addresses) In some cases, you
do not want people to access your computer or you want to restrict certain
individuals from accessing your computer or server
Range :
Class A (Netid.hostid.hostid.hostid) : 1.0.0.0 to 126.0.0.0
Class B (Netid.Netid.hostid.hostid) : 128.0.0.0 to 191.0.0.0
Class C (Netid.Netid.Netid.hostid) : 192.0.0.0 to 223.0.0.0
Class D (Multicast) : 224.0.0.0 to 239.0.0.0
Class E (For Research) : 240.0.0.0 to 255.0.0.0
private IP address
These addresses are not routable on the public Internet. Or
are behind the router.
Using a private IP address will make your computer
invisible to certain types of network attacks; however, you
will not be able to easily establish your computer as a
server.
Private Intranet addresses cannot be sent over the Internet.
If an Internet router receives a packet with either a source
or destination address that is reserved, it will drop the
packet.
reserved IP address space for private network
Class A
Class A network IP address range = 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
For one Class A network:
Subnet mask = 255.0.0.0
Network address length = 8 bit
Computer address length = 24 bit
Host in one network = 16777216-2
Class B
Class B network IP address range = 172.16.0.0 - 172.16.255.255
Class B network IP address range = 172.17.0.0 - 172.17.255.255
Class B network IP address range = 172.18.0.0 - 172.18.255.255
…....
Class B network IP address range = 172.31.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
For each of the 16 Class B networks:
Subnet mask = 255.255.0.0
Network address length = 16 bit
Computer address length = 16 bit
Class C
Class C network IP address range = 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.0.255
Class C network IP address range = 192.168.1.0 – 192.168.1.255
Class C network IP address range = 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.2.255
…
Class C network IP address range = 192.168.255.0 - 192.168.255.255
For each of the 256 Class C networks:
Subnet mask = 255.255.255.0
Network address = 24 bit
Computer address = 8 bit
Blocks in IP Classes
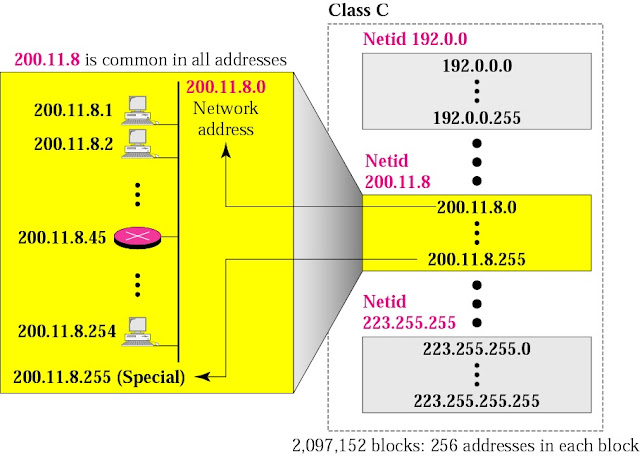 |
| Blocks in IP Classes |
IPv6 address Format
2001:0DA8:E800:0010208: 0b2it6s0:3EFF:FE47:0001
- 8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits
- Each group represents 16 bits
- Separator is “:”
- Case-independent
0010000111011010 0000000011010011 0000000000000000
0010111100111011 0000001010101010 0000000011111111
1111111000101000 1001110001011010
21DA:00D3:0000:2F3B:02AA:00FF:FE28:9C5A
 |
| IPv6 address Format |
Leading zero censorship
FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:2
FF02::2
(8 − 2) × 16 = 96





























